Since September 1, 2018, high voltage halogen work lights no longer comply with the requirements set by the European Union for lighting use and energy consumption. While halogen work lights are often equipped with a C or D energy label, the European Union stipulates that the lamps must have at least a label B. Therefore, a good alternative to halogen work lights is LED work lights
Despite the fact that this measure does not yet apply to low-voltage halogen lamps and the fact that halogen worklights are still available in many places, we still recommend that you make the switch to LED worklights. There are more differences between the two types of worklights than just their energy consumption. These differences will be further explained below.

1. Energy consumption
Zoals hierboven al kort geïntroduceerd zit er veel verschil in het energieverbruik van een halogeen werklampen en een LED werklamp. Het grote voordeel van LED werklampen ten opzichte van halogeen werklampen is het gereduceerde energieverbruik. Volgens de NOS verbruikt een halogeen werklamp 75% meer energie dan een LED werklamp. Daarnaast zorgt traditionele verlichting ook voor meer CO2-uitstoot. Naast het energieverbruik stoten de halogeen werklampen ook veel warmte uit. Dit komt doordat de lamp ongeveer 30% van het stroomverbruik om zet in licht.
The use of traditional lighting leads to increased CO2 emissions. According to Milieu Centraal, LED lamps consume 75 percent less electricity than halogen lamps and 85 percent less than incandescent lamps. – NOS
2. Safety
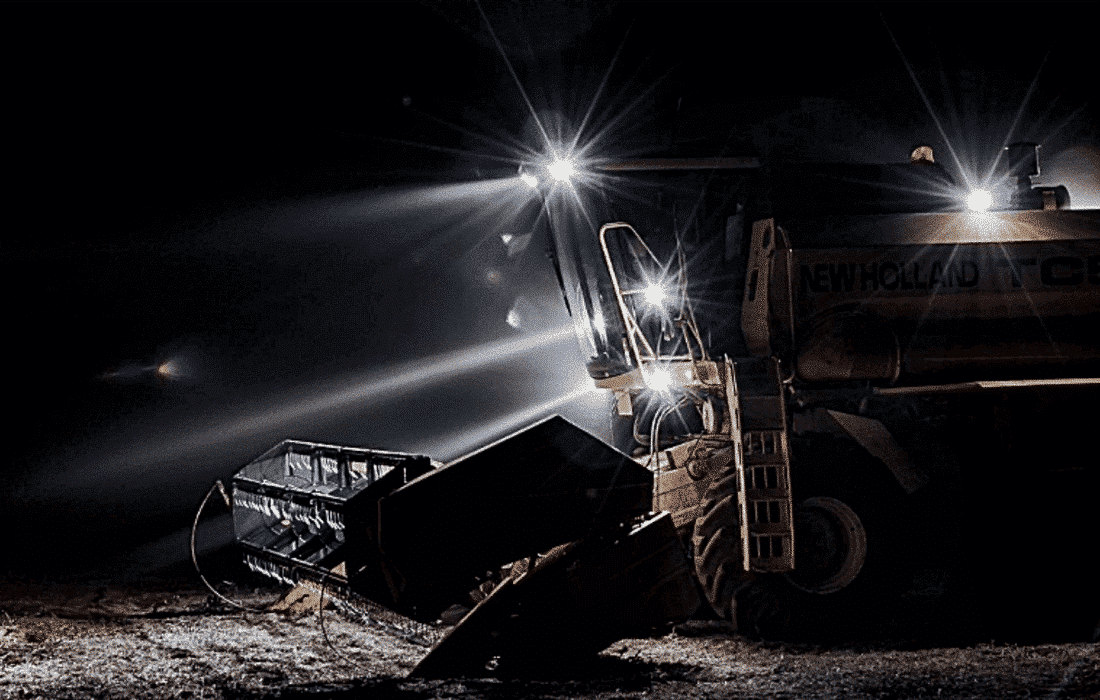
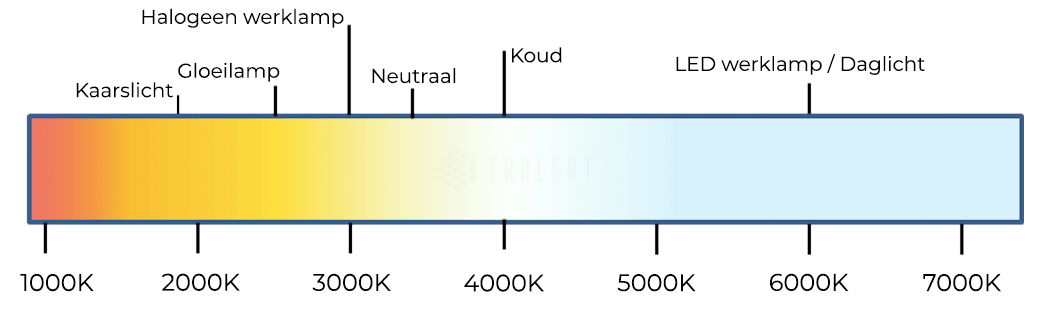
Besides the difference in energy consumption, it is good to make the comparison between the different light colors. The LED worklight produces a light color that can be compared to the general color of daylight. In contrast, the halogen worklight emits a dark, warm light color. Practice has shown that this warm color works less efficiently.
Due to the warm light color emitted by halogen work lights, the human eyes get tired faster. This is a lot less with LED lighting, as the light color of LED work lights is very similar to daylight. To prevent accidents, we therefore strongly recommend companies to use LED work lights. This will improve safety on the road.
3. Sustainability
The lifespan of LED worklights as opposed to halogen worklights is enormous. Where a halogen lamp lasts about 500 hours (12.5 working weeks), the LEDs from a good LED worklight can last up to 50,000 hours. In some cases this is even longer than the machine on which the LED worklight is mounted.
Besides the fact that these developments in the field of LED lighting make a good contribution to the world of tomorrow, this development also ensures a reduction in costs. When the standard halogen worklight has reached its number of hours, it must be replaced. There are costs associated with this. In addition to the new lamps that must be ordered, there are also costs associated with replacing the lighting. With the advent of LED worklights, these are completely history.
4. Difference in form
Because the bulbs used in the LED work lights are smaller than halogen bulbs, the smaller in size LED work lights also have a good light output. In addition, the reduction in size of the bulbs ensures that the LED lamps have a higher light density.
Despite the light density of LED worklights, the light distribution of an LED worklight is much better than that of a halogen worklight. When using a halogen worklight, you will notice that the 'wick' of the light is well lit, but around the 'wick' the light distribution quickly diminishes.
5. Difference in price
If we compare the purchase price of the two types of lamps, the LED lamp costs the most. However, it also delivers by far the most value. Thus, when using LED worklights, you save on power consumption, mounting the lights and also contribute to a better world tomorrow.
As described above, an LED worklight already saves 75% of its power compared to a halogen worklight. In the long run, this investment will therefore often pay for itself. This is partly due to the number of burning hours. But what is the exact payback period of LED lighting?
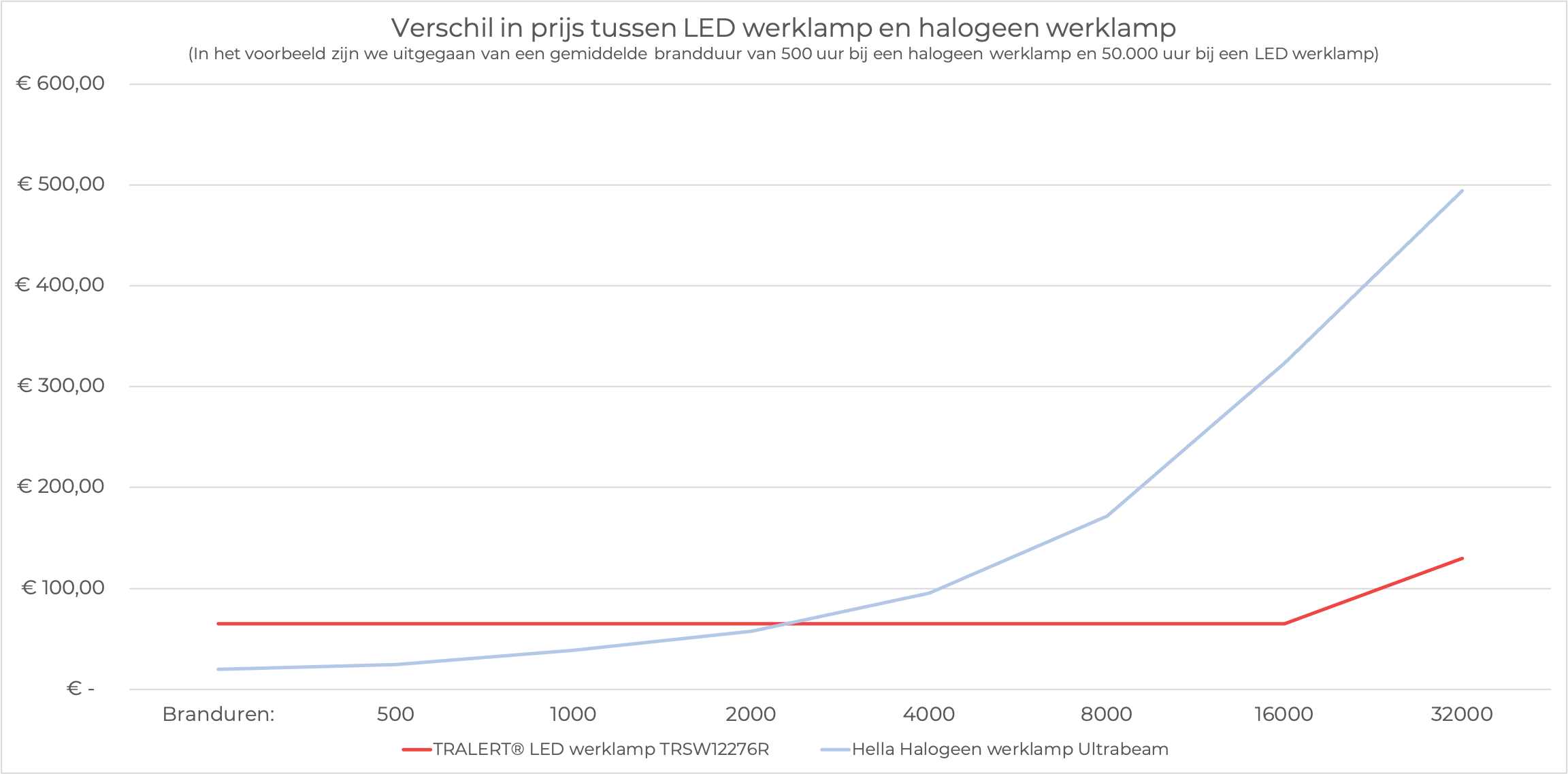
The example above clearly shows the difference in price between the different work lights. In the example we have compared the TRALERT® LED worklight TRSW12276R with the Hella Ultra Beam worklight.
In the example, we assumed 500 hours of operation for a Halogen worklight and 50,000 hours for an LED worklight. As can be seen from the above graph, the LED worklight is more expensive than the halogen worklight. However, the LED worklight earns itself back over time compared to the halogen worklight.
After approximately 2200 hours, the LED worklight is cheaper than the halogen worklight. In the example, we have not taken into account the replacement of the halogen H3 lamp. This makes that the LED lighting in reality has a shorter payback period than the estimated 2200 hours.
Do you have a specific question about the differences between LED work lights and halogen work lights?
If you have specific questions about the differences between the two types of work lamps, feel free to contact our technical support. They are available daily to provide you with the right answers.